This guide focuses on pure electric vehicles, also known as BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles – figure 1.). This classification is often recognised as pure or fully electric vehicles, powered solely by an integrated battery pack that is charged from a slow charge domestic wall box, fast charge street charging post or rapid charger. For this reason, pure electric EVs are also referred to as plug-ins.
Generally, all EVs have either one or two electric motors rather than an internal combustion engine. Some EVs actually have combined motors built into their hubs, on all 4 wheels. All EVs use a large traction battery pack to power the electric motor and must be plugged in to a charging station or wall outlet to charge. Because it runs on electricity, the vehicle emits no exhaust from a tailpipe and does not contain the normal liquid fuel mechanics, such as a fuel line, fuel tank, or fuel pump.
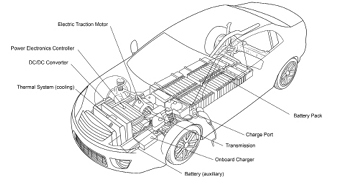
EV OVERVIEW
- » Auxiliary Battery: In an electric drive vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides 12V electricity to power vehicle accessories.
- » Charge Port: Enables the vehicle to connect to an external AC or DC power supply to charge the traction battery pack.
- » DC/DC converter: This device converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to reduce to lower-voltage 12V DC voltage needed to power the vehicle accessories and to recharge the auxiliary battery.
- » Electric traction motor: Powered by the system battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle’s wheels. Many new EVs are equipped with motor generators that function as both drive and regeneration/braking.
- » Onboard charger: Fed by incoming AC power supplied via slow and fast charge units, the onboard charger then converts AC to DC power for charging the main battery. It manages battery functions such as current, voltage, state of charge, and temperature whilst charging the main battery pack.
- » Power electronics controller: This unit controls the flow of electrical energy delivered by the main battery, controlling speed of the main drive motor/s and the torque or power that it produces.
- » Thermal cooling system: This system sustains the correct operating temperature range of the electric motor, power electronics, and other temperature sensitive components.
- » Traction battery pack: Stores electricity for use by the propulsion system.
- » Transmission: The transmission provides mechanical power taken from the electric traction motor to drive the wheels.